Introduction
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by inflammation and infection of the gums and the supporting structures of the teeth. Without proper treatment, gum disease can lead to tooth loss and have negative impacts on overall health.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and consequences of gum disease. We will also discuss various treatment options and preventive measures that can help manage and alleviate the symptoms of gum disease. Additionally, we will provide insights into the best mouthwash and toothpaste options that can complement your oral hygiene routine and contribute to the prevention and treatment of gum disease.
Want a fast and easy teeth-whitening solution to get a brighter, healthier smile in no time, read the bonus tip at the bottom of the page.
Table of Contents
5/ The Role of Mouthwash and Toothpaste
7/ Additional Tips for Oral Health
8/ The Link Between Gum Disease and Overall Health
Understanding Gum Disease
What is Gum Disease?
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, is an inflammatory condition that affects the gums and the supporting structures of the teeth. It begins with the accumulation of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. If not removed through proper oral hygiene practices, plaque can harden into tartar, leading to gum inflammation and infection.
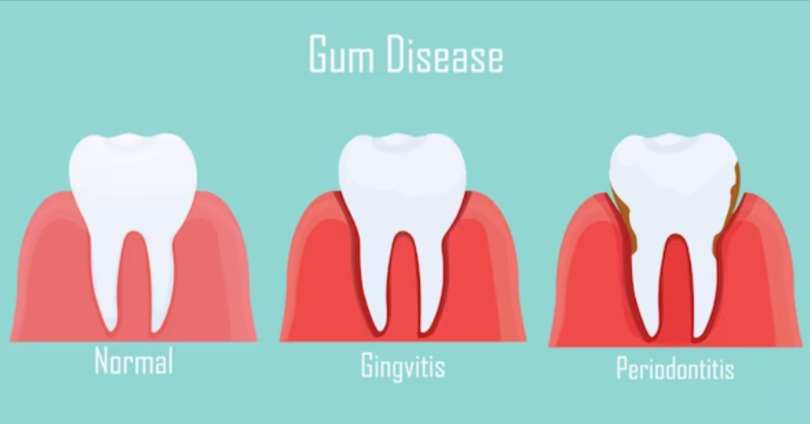
Gum disease progresses in stages, starting with gingivitis, which is the mildest form of the condition. If left untreated, gingivitis can develop into periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease that can cause irreversible damage to the gums, bone, and teeth.
Causes of Gum Disease
The primary cause of gum disease is the accumulation of plaque and tartar due to inadequate oral hygiene practices. However, several factors can increase the risk of developing gum disease, including:
- Smoking and tobacco use
- Poor oral hygiene
- Hormonal changes (such as pregnancy or menopause)
- Diabetes
- Genetic predisposition
- Certain medications
- Medical conditions that weaken the immune system
- Poor nutrition
Consequences of Gum Disease
If left untreated, gum disease can have serious consequences for oral health. It can lead to:
- Gum recession and tooth loss
- Bone loss in the jaw
- Abscesses or infections
- Chronic bad breath
- Changes in the bite or tooth alignment
In addition to oral health complications, gum disease has been associated with an increased risk of systemic conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Signs of Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease and is characterized by inflammation of the gums. Common signs and symptoms of gingivitis include:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing
- Bad breath or a persistent bad taste in the mouth
- Receding gums
- Formation of pockets between the teeth and gums
Identifying Periodontitis
Periodontitis is an advanced form of gum disease that occurs when the infection spreads below the gum line and damages the supporting structures of the teeth. In addition to the symptoms of gingivitis, periodontitis can cause:
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Changes in the way teeth fit together when biting
- Pus around the gums or teeth
- Pain or discomfort while chewing
Pictures of Gum Disease
Visualizing the symptoms of gum disease can provide a better understanding of the condition. You can refer to the CDC’s Oral Health website for pictures and illustrations that depict the various stages and manifestations of gum disease.
Treatment Options
Professional Treatments
If you have gum disease, seeking professional dental treatment is essential to halt the progression of the condition and prevent further damage. Common professional treatments for gum disease include:
- Scaling and root planing: This deep cleaning procedure involves removing plaque and tartar from below the gum line and smoothing the tooth roots to promote healing and prevent bacteria buildup.
- Periodontal surgery: In advanced cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair damaged gums, remove infected tissue, and regenerate lost bone.
- Antibiotics: Your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to control bacterial infection and reduce inflammation.
At-Home Remedies
In conjunction with professional treatment, adopting good oral hygiene practices at home can help manage gum disease. These include:
- Brushing: Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Be sure to brush along the gumline to remove plaque and bacteria effectively.
- Flossing: Clean between your teeth daily using dental floss or interdental brushes to remove plaque and debris from areas that a toothbrush can’t reach.
- Mouthwash: Rinse with an antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce bacteria and control plaque buildup. Choose a mouthwash specifically formulated for gum health.
- Healthy lifestyle: Maintain a balanced diet, limit sugary and acidic foods, avoid smoking, and manage stress to support overall oral health.
Natural Remedies
Some natural remedies may complement traditional treatments and promote gum health. These include:
- Oil pulling: Swishing coconut oil or sesame oil in your mouth for several minutes may help reduce harmful bacteria and improve gum health.
- Saltwater rinse: Rinsing your mouth with warm saltwater can help reduce inflammation and soothe gum discomfort.
- Herbal remedies: Certain herbs, such as tea tree oil and aloe vera, have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties that may benefit gum health. Use these remedies with caution and consult with your dentist or healthcare provider before use.
Preventing Gum Disease
Maintaining Good Oral Hygiene
Practicing good oral hygiene is crucial for preventing gum disease. Follow these oral hygiene tips to keep your gums healthy:
- Brush your teeth thoroughly at least twice a day using a fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristled toothbrush.
- Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and along the gumline.
- Use an antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce bacteria and freshen your breath.
- Replace your toothbrush every three to four months or sooner if the bristles become frayed.
Dietary Considerations
A healthy diet plays a vital role in maintaining gum health. Consider the following dietary guidelines:
- Limit sugary and acidic foods and beverages, as they can contribute to plaque formation and tooth decay.
- Include plenty of fruits and vegetables in your diet, as they provide essential vitamins and minerals that support gum health.
- Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated and promote saliva production, which helps wash away food particles and neutralize acid.
Regular Dental Check-ups
Regular dental check-ups are essential for early detection and prevention of gum disease. Visit your dentist at least once a year, or more frequently if recommended, for professional cleanings and examinations. Your dentist can identify signs of gum disease and provide appropriate treatments or referrals.
The Role of Mouthwash and Toothpaste
Choosing the Right Mouthwash
Mouthwash can be a valuable addition to your oral hygiene routine, especially when dealing with gum disease. When selecting a mouthwash, consider the following factors:
- Antibacterial properties: Look for a mouthwash that contains antibacterial ingredients like chlorhexidine or essential oils such as tea tree oil or peppermint oil.
- Alcohol-free: Alcohol can cause dry mouth, which may worsen gum disease symptoms. Choose an alcohol-free mouthwash to avoid this potential side effect.
- Fluoride content: Some mouthwashes contain fluoride, which can help strengthen tooth enamel and prevent tooth decay. This can be beneficial for individuals with gum disease who may be at increased risk of cavities.
Selecting the Best Toothpaste
Choosing the right toothpaste is crucial for maintaining oral health, especially when dealing with gum disease. Consider the following factors when selecting a toothpaste:
- Antigingivitis properties: Look for toothpaste that is specifically formulated to prevent and treat gingivitis. These toothpastes often contain ingredients like stannous fluoride or triclosan.
- Fluoride content: Choose a toothpaste that contains fluoride to help strengthen tooth enamel and protect against cavities.
- Sensitive teeth: If you have sensitive gums or teeth, consider using a toothpaste designed for sensitive teeth to minimize discomfort during brushing.
The Benefits of Fluoride
Fluoride is a mineral that has been proven to strengthen tooth enamel and prevent tooth decay. Using fluoride toothpaste and mouthwash can be particularly beneficial for individuals with gum disease, as they may be at increased risk of cavities due to the compromised health of their gums.
Alternative Approaches
Oil Pulling
Oil pulling is an ancient practice that involves swishing oil in the mouth to promote oral health. Advocates of oil pulling claim that it can reduce harmful bacteria, plaque, and inflammation. While scientific evidence supporting the benefits of oil pulling for gum disease is limited, some individuals find it to be a valuable addition to their oral hygiene routine. It is important to note that oil pulling should not replace traditional dental care.
Herbal Mouthwashes
Herbs like tea tree oil, aloe vera, and chamomile have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties that may benefit gum health. Some commercially available herbal mouthwashes combine these ingredients to provide a natural alternative to traditional mouthwashes. However, it is important to consult with your dentist or healthcare provider before using herbal mouthwashes to ensure they are safe and effective for your specific needs.
Natural Toothpaste Options
For those seeking natural alternatives to conventional toothpaste, several natural toothpaste options are available. These toothpastes often contain ingredients like baking soda, essential oils, and herbal extracts that provide antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory benefits. While natural toothpaste can be a suitable choice for individuals with gum disease, it is important to ensure that they contain fluoride to protect against tooth decay.
Additional Tips for Oral Health
Proper Brushing Techniques
To ensure effective plaque removal and gum health, follow these proper brushing techniques:
- Hold your toothbrush at a 45-degree angle to the gumline.
- Use gentle, circular motions to brush the outer and inner surfaces of your teeth.
- Pay attention to the chewing surfaces and brush them using back-and-forth motions.
- Brush your tongue gently to remove bacteria and freshen your breath.
Flossing and Interdental Cleaning
Flossing and interdental cleaning are essential for removing plaque and debris from between the teeth and along the gumline. Follow these steps for proper flossing:
- Use a piece of dental floss approximately 18 inches long.
- Gently slide the floss between your teeth, curving it around each tooth in a C-shape.
- Move the floss up and down to remove plaque and debris.
- Repeat this process for each tooth, using a clean section of floss each time.
In addition to traditional flossing, interdental brushes and water flossers can be effective alternatives for cleaning between teeth and along the gumline.
Regular Dental Examinations
Regular dental examinations are essential for maintaining oral health and preventing gum disease. Your dentist can detect early signs of gum disease and provide appropriate treatment. During your dental visits, your dentist will perform a thorough examination, clean your teeth, and assess your overall oral health.
The Link Between Gum Disease and Overall Health
Gum disease is not only a concern for oral health; it has also been linked to various systemic conditions. Research suggests that gum disease may contribute to the development or worsening of the following health issues:
- Cardiovascular disease: The bacteria associated with gum disease can enter the bloodstream and contribute to the formation of plaques in the arteries, potentially increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Diabetes: Gum disease can make it more difficult to control blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes, and poorly controlled diabetes can worsen gum disease.
- Respiratory infections: The bacteria from gum disease can be inhaled into the lungs, potentially leading to respiratory infections such as pneumonia.
Maintaining good oral hygiene and seeking timely dental care are crucial for preventing gum disease and reducing the risk of associated systemic conditions.
Conclusion
Gum disease is a common oral health condition that can have significant consequences if left untreated. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help individuals prevent and manage gum disease effectively. Incorporating effective oral hygiene practices, including the use of appropriate mouthwash and toothpaste, is essential for maintaining gum health. By following these guidelines and seeking regular professional dental care, individuals can take proactive steps to preserve their oral health and overall well-being.
Remember, if you experience any symptoms of gum disease or have concerns about your oral health, consult with your dentist or healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Bonus Tip
Ready to achieve a brighter, healthier smile the natural way? Try our all-natural teeth whitening product today and experience the benefits of a chemical-free, eco-friendly solution. With no harsh chemicals or additives, our product can help you achieve a brighter, whiter smile while promoting overall dental health. Learn more here!